The landscape of infusion therapy is rapidly evolving, making the decision between home-based and facility-based care more critical than ever.
For physicians, infusion nurses, and healthcare administrators, this choice impacts patient safety, comfort, and overall treatment efficiency.
Home infusion offers convenience and personalized care, often preferred for chronic conditions, while facility-based infusion provides structured oversight and immediate access to medical resources, ideal for complex or high-risk treatments.
The key lies in understanding the unique needs of each patient and aligning them with the appropriate care setting.
This guide explores the factors driving these decisions, equipping healthcare professionals and business leaders with actionable insights to deliver better outcomes.
By balancing clinical expertise with patient-centered care, infusion management teams can optimize both experiences and results.
The Evolving Landscape of Infusion Therapy
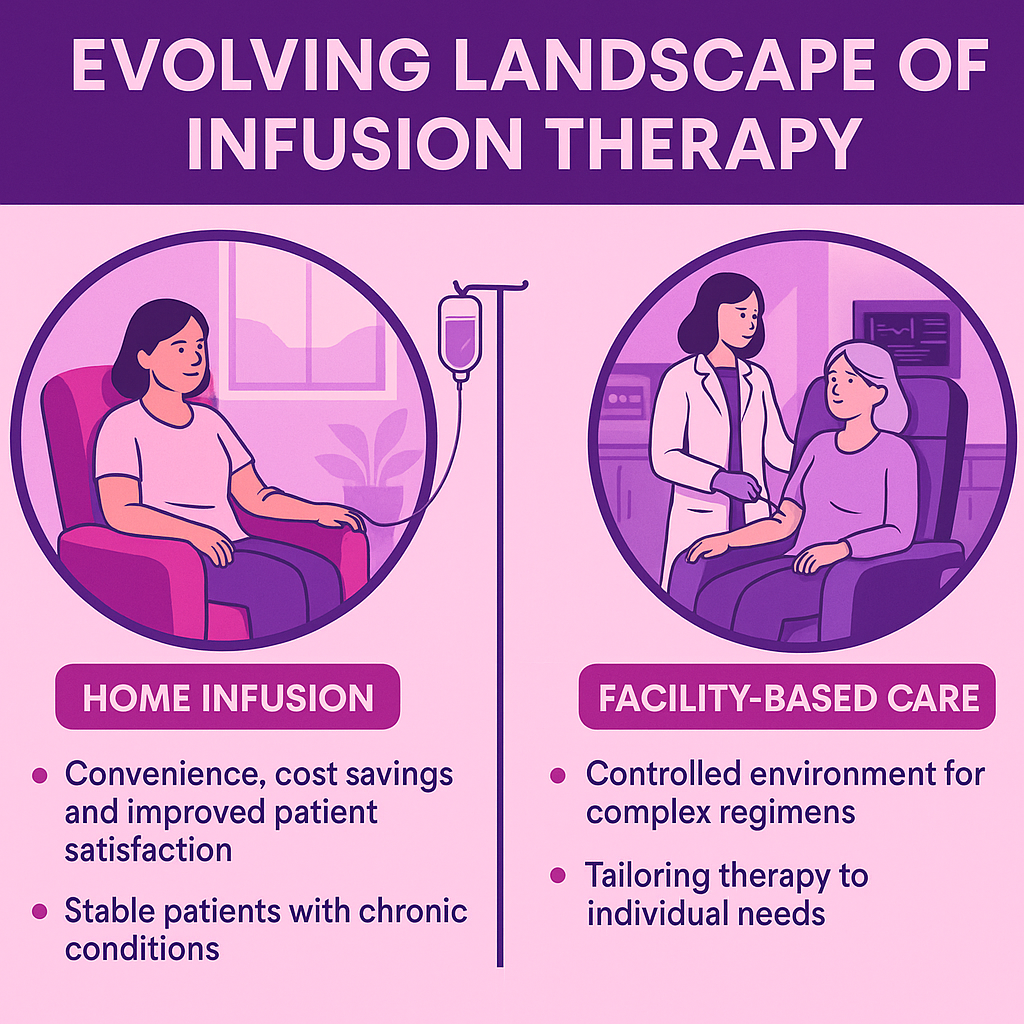
Advancements in medical technology and the growing emphasis on patient-centered care are transforming the delivery of infusion therapy.
Home infusion therapy is emerging as a viable alternative to facility-based care, offering convenience, cost savings, and improved patient satisfaction.
However, determining the appropriate setting is critical to achieving optimal outcomes.
For example, patients requiring complex regimens may benefit from the controlled environment of an infusion center, while stable patients with chronic conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or infections can safely receive treatment at home.
Leveraging innovative tools, clinical expertise, and care coordination allows healthcare teams to tailor infusion therapy to meet individual needs.
This approach not only enhances quality of care but also supports better resource allocation across the healthcare system.
Clinical Considerations
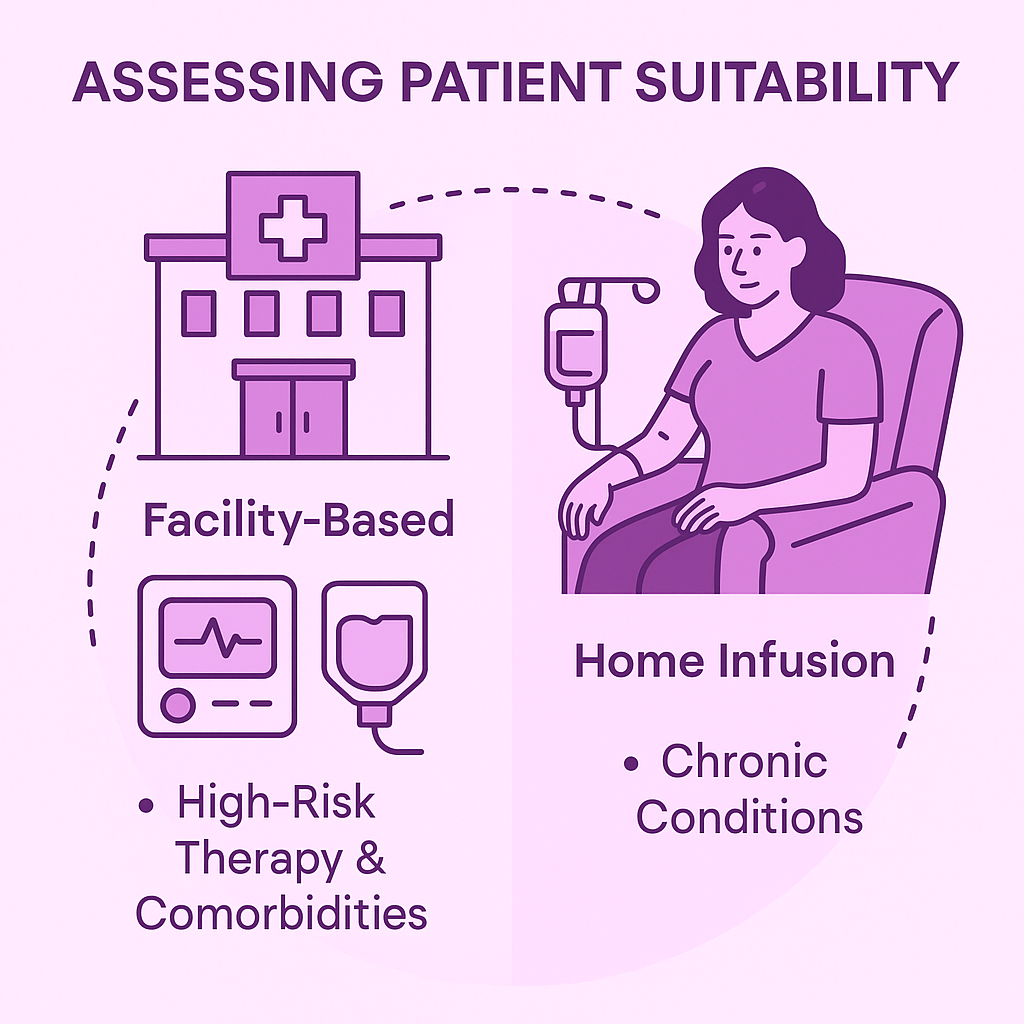
Assessing Patient Suitability
Effective infusion management starts with placing the patient in the right care setting, balancing safety, convenience, and resource efficiency.
High-risk therapies like CAR-T cell treatments require facility-based administration due to the potential for severe adverse events, which demand immediate intervention.
On the other hand, stable patients with chronic conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or multiple sclerosis, may benefit from home infusion.
This approach not only improves patient comfort but can also reduce healthcare costs by up to 30%, as reported by recent studies.
However, success hinges on proper patient selection—ensuring they have a reliable support system and no contraindications for home-based care.
Additionally, patients with complex comorbidities may require closer monitoring in clinical settings to prevent complications.
Collaboration among interdisciplinary teams and leveraging technology, such as real-time monitoring tools, can further enhance outcomes and streamline workflow, ensuring high-quality, patient-centered care.
Reference: Infusion therapy: A model for safe practice in the home setting
Home Environment Assessment
Ensuring Safety and Compliance
Effective home infusion therapy starts with a thorough home assessment to ensure safety, efficiency, and optimal patient outcomes.
The environment must support the therapy, including adequate space, cleanliness, and reliable access to utilities like power and water.
Emergency preparedness is non-negotiable—emergency equipment and clear protocols for adverse reactions should always be in place.
Equally critical is caregiver support; trained caregivers can provide essential monitoring and assistance, reducing the risk of complications.
According to recent data, home infusion therapy not only improves patient comfort but can also reduce hospital stays by up to 70%, highlighting its value in healthcare management.
By aligning the right infrastructure, preparation, and support, healthcare teams can deliver high-quality infusion care while empowering patients in the comfort of their own homes.
Reference: General Recommendations for Most Home Infusion Patients
Psychological and Emotional Benefits
The Comfort of Home
Effective infusion management begins with a patient-centered approach, ensuring treatment plans are tailored to individual needs while maintaining high safety standards.
One best practice is comprehensive pre-infusion assessment, which evaluates patient suitability for home-based care, minimizing potential risks.
Strong communication among physicians, infusion nurses, and healthcare teams is critical for seamless care coordination, ensuring medication protocols are followed accurately and any adverse reactions are swiftly addressed.
For instance, leveraging nurse-guided education on infusion techniques and equipment maintenance can reduce complications and hospital readmission rates.
Studies show that well-implemented home infusion programs can improve patient satisfaction by over 70%, underscoring their role in enhancing overall care experiences.
Additionally, regular monitoring through virtual check-ins or in-home visits ensures adherence to treatment and mitigates concerns early.
By prioritizing collaboration, education, and technology, infusion teams can deliver care that is both effective and compassionate.
Home infusion therapy offers significant psychological advantages:
- Reduced Anxiety: Familiar surroundings can alleviate stress associated with clinical environments.
- Enhanced Well-being: Being close to family and in a comfortable setting can improve overall mental health.
- Increased Autonomy: Patients often feel more in control of their treatment schedules and daily routines.
Reference: Why Patients Prefer Home IV Infusion Therapy
The Role of Dedicated Nursing Support in Home Infusion
Trust and Rapport
Effective infusion management requires a collaborative, patient-centered approach to optimize outcomes and improve care delivery.
Building trust and rapport with patients is a cornerstone of success, as it fosters open communication and increases adherence to treatment plans.
Infusion nurses and clinicians should prioritize clear, empathetic explanations of procedures, addressing patient concerns to alleviate anxiety and ensure informed consent.
Streamlining workflows through technology, such as infusion-specific software, reduces errors and enhances efficiency.
A study published in the Journal of Infusion Nursing highlights that facilities using automated infusion pumps reported a 34% reduction in medication errors.
Regular training for staff on updated protocols and equipment ensures consistency in care and safety.
Multidisciplinary collaboration is key—physicians, nurses, and management teams must align on goals, emphasizing continuous improvement and patient satisfaction.
Personalized Education
Effective infusion management requires a blend of clinical expertise, patient-centered care, and operational efficiency.
For healthcare teams, the key lies in adopting best practices that prioritize safety and optimize outcomes.
One critical element is thorough patient assessment before each infusion, ensuring accurate dosing and minimizing the risk of adverse reactions.
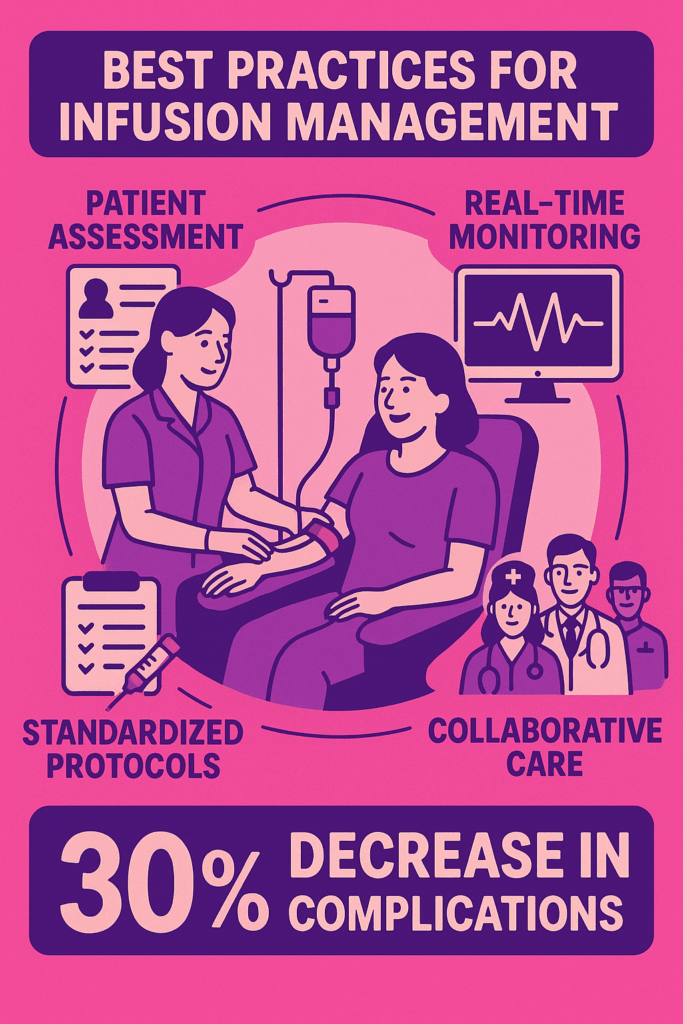
Incorporating real-time monitoring tools can further enhance safety by detecting complications early.
Collaboration between physicians, infusion nurses, and assistants is vital to streamline workflows and reduce errors.
For example, implementing standardized protocols for medication preparation and administration can significantly improve consistency and reduce variability in care delivery.
According to recent studies, facilities that invest in training and standardized procedures report up to a 30% decrease in infusion-related complications.
By focusing on clear communication, advanced technologies, and evidence-based practices, healthcare teams can provide seamless, high-quality infusion care tailored to each patient’s needs.
Early Detection
Effective infusion management is a cornerstone of quality patient care, requiring a balance of clinical precision and proactive monitoring.
Early detection of complications, such as infection or infiltration, is critical. Regularly assessing infusion sites and devices can significantly reduce adverse events, improving patient safety and outcomes.
According to recent studies, up to 60% of central line-associated bloodstream infections (CLABSIs) are preventable with proper protocols, such as aseptic technique and timely catheter changes.
Collaboration is equally important.
Physicians, infusion nurses, and PAs should communicate frequently to adjust treatment plans based on patient response.
Using technology, like smart infusion pumps, can enhance accuracy in dosage delivery while reducing errors.
By prioritizing training, leveraging technology, and fostering team coordination, healthcare teams can optimize infusion therapy, minimizing risks and maximizing effectiveness for their patients.
Reference: Home Infusion Therapy: Understanding Benefits, Challenges, and Eligibility
Technological Requirements
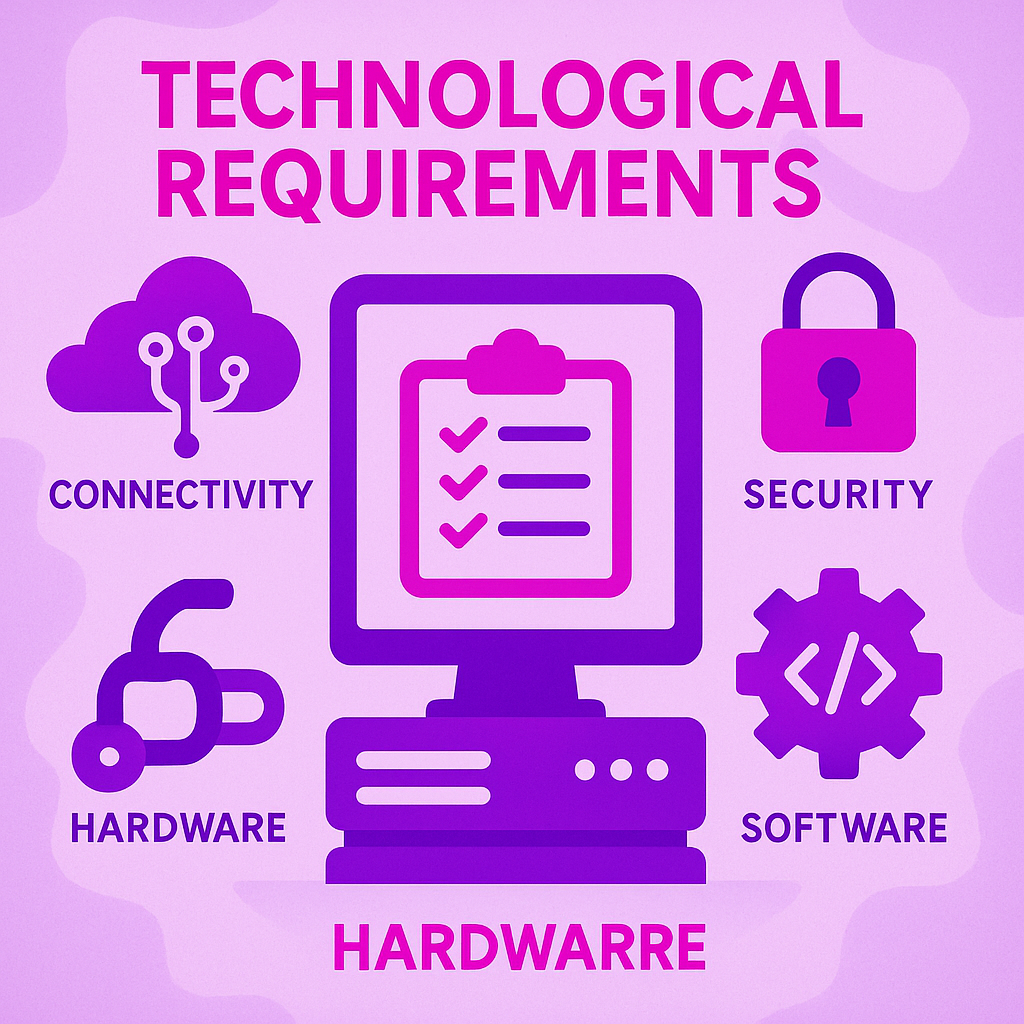
Implementing appropriate technology is vital for effective home infusion therapy:
Infusion Equipment
Effective infusion management hinges on selecting the right equipment and implementing best practices to ensure patient safety and treatment success.
Portable infusion pumps, designed for home use, have revolutionized care, offering patients greater mobility and comfort.
For clinicians, these devices improve workflow efficiency by reducing hospital dependency.
However, ensuring optimal outcomes requires considering key factors like device accuracy, compatibility with various infusion therapies, and patient education.
For example, smart pumps with dose-error reduction systems have been shown to decrease medication errors by up to 73%, according to recent studies.
Additionally, regular maintenance protocols and user training are critical to minimizing malfunctions or misuse.
By prioritizing high-quality equipment and comprehensive training, healthcare teams can deliver safer, more effective infusion therapy, improving both patient satisfaction and clinical outcomes.
Telehealth Integration

Effective infusion management requires a blend of clinical expertise, efficient processes, and patient-centered care.
One key practice is incorporating multidisciplinary collaboration—physicians, infusion nurses, and physician assistants working together to tailor treatments based on individual patient needs.
Utilizing electronic health records (EHRs) can streamline workflows by tracking medication administration and ensuring accurate dosing, reducing errors.
Additionally, integrating telehealth for remote monitoring allows teams to evaluate patient responses in real-time, reducing unnecessary clinic visits while maintaining consistent care.
Several case studies and operational reports confirm that implementing advanced scheduling tools-such as iQueue for Infusion Centers-has led to significant improvements in patient throughput and chair utilization.
For example, Penn Medicine’s Abramson Cancer Center reported a 25% increase in patient volumes and a 20% increase in patient hours after deploying such a system 3.
Other centers have reported similar gains, with increases in patient volumes ranging from 14% to 25% and notable improvements in chair utilization and reductions in wait times
However, maintaining compliance with safety protocols like USP <800> is crucial to protect both staff and patients.
Ultimately, embracing technology, fostering teamwork, and prioritizing patient safety are the pillars of successful infusion management, enabling better outcomes and a smoother care experience.
Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
Effective infusion management is critical for delivering safe, high-quality care while optimizing workflow efficiency.
Better practices begin with standardized protocols to ensure consistency and reduce errors, particularly in medication preparation and administration.
Utilizing Electronic Health Records (EHRs) for real-time documentation enhances communication between care teams, helping to track infusion schedules, dosages, and patient progress seamlessly.
Incorporating smart infusion pumps with dose-error reduction systems further minimizes risks, ensuring precise medication delivery.
Equally important is staff training.
Regular education on emerging therapies, infusion technologies, and safety measures empowers teams to stay current and confident in their roles.
For example, a 2023 study highlighted that infusion centers implementing automated scheduling systems saw a 20% reduction in patient wait times, improving overall satisfaction.
Prioritizing patient-centered care, efficient resource utilization, and ongoing team collaboration leads to better outcomes and a more streamlined infusion process.
Reference: Home Infusion Pharmacy Services – ASHP
Emergency Preparedness
Planning for the Unexpected
Emergency preparedness in healthcare is not just a regulatory necessity—it’s a decisive factor in ensuring patient safety, minimizing operational disruption, and instilling confidence among healthcare teams.
For infusion centers, where daily operations are highly dependent on timely medication delivery, power stability, and staffing efficiency, a well-thought-out emergency plan becomes even more essential.
Preparing for events like natural disasters, power outages, staffing shortages, or patient surges requires a proactive, coordinated effort involving the entire healthcare team—from physicians and nurses to pharmacy and administrative staff.
One of the key components of a robust emergency preparedness strategy is maintaining an uninterrupted supply chain.
For example, ensuring sufficient stock of infusion therapies, backup generators for critical equipment, and remote access to electronic health records (EHRs) can mitigate the risks associated with unexpected disruptions.
Additionally, conducting regular team training on emergency protocols helps healthcare professionals feel prepared and empowered when faced with high-stress situations.
This can include mock drills simulating scenarios such as evacuations, IT system failures, or patient overflow, allowing the team to identify and address potential gaps in response.
Collaborative communication is also vital. A clear, well-documented communication plan ensures that staff members know their roles, how to reach key stakeholders, and the steps to escalate critical issues.
Working closely with local emergency services, community partners, and public health organizations can create a broader safety net to support patients during unforeseen crises.
Ultimately, successful emergency preparedness combines strategic planning, continuous education, and strong partnerships, prioritizing the well-being of both patients and staff.
By fostering a culture of readiness, infusion centers can confidently adapt to challenges, ensuring compassionate, uninterrupted care even in the most trying of circumstances.
Reference: Infusion therapy: A model for safe practice in the home setting
Evaluating Financial Implications
Effective infusion management requires a balance of clinical precision and patient-centered care. Home infusion therapy is a growing alternative to hospital care, offering clear benefits.
For patients, it reduces the need for hospitalization, cutting costs substantially.
Multiple peer-reviewed studies and industry analyses report substantial cost reductions with home infusion.
For example, the National Home Infusion Association (NHIA) review found that home infusion can save between $40,460 and $120,500 per patient for certain therapies when compared to inpatient care 23.
Per-day cost comparisons show home infusion at $122–$225 versus $586–$798 for inpatient settings, representing a savings of roughly 60%–85% per day for some treatments 23.
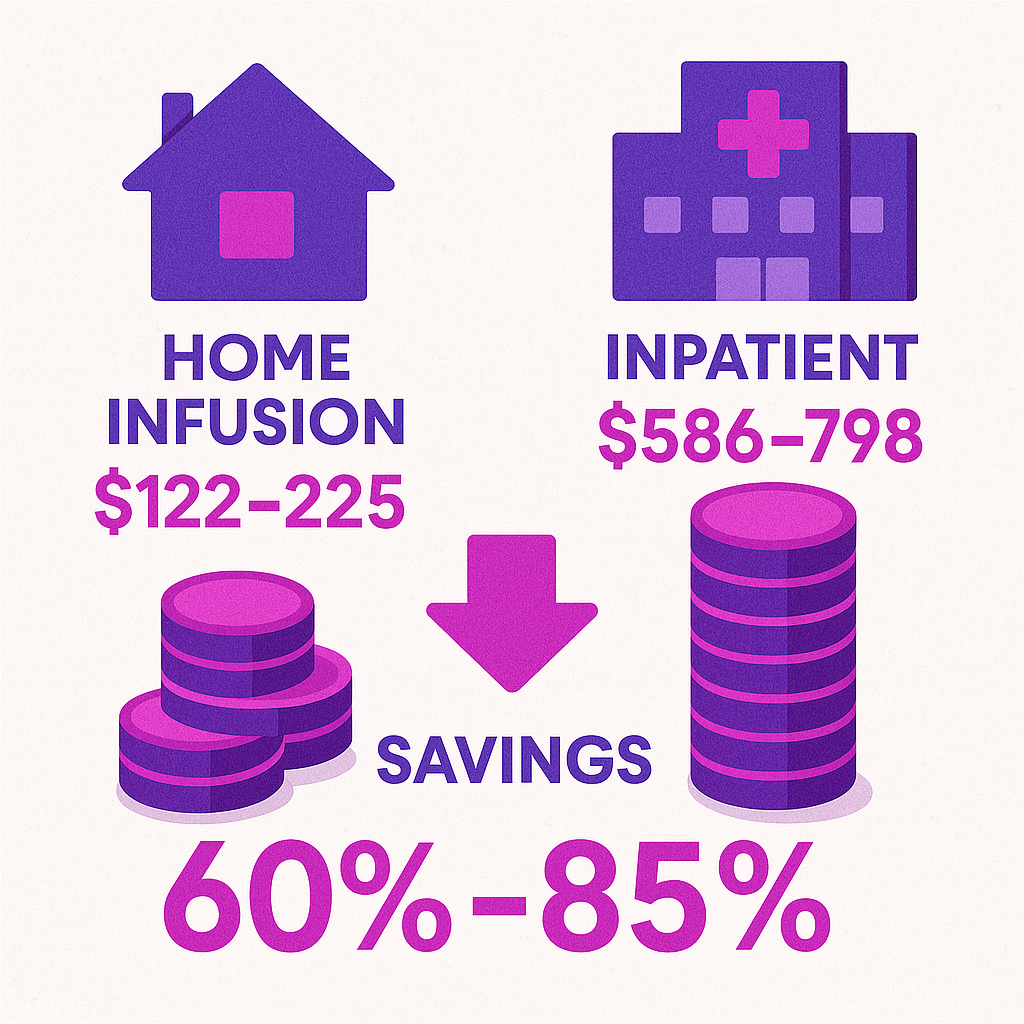
Another study cited in the Journal of General Internal Medicine found that patients receiving care at home incurred 52% less in medical expenses than those hospitalized overnight 3.
It also minimizes disruptions to daily life, allowing patients to recover in a familiar setting while avoiding extensive travel.
For healthcare teams, best practices include thorough patient assessments, robust care coordination, and leveraging innovative technologies like remote monitoring to enhance safety and compliance.
Ensuring proper staff training for infusion protocols and maintaining clear communication with patients about medication adherence are crucial.
As demand rises, home infusion represents a cost-effective, patient-friendly solution that aligns with evolving healthcare trends.
Reference: Cost Savings: Home Versus Inpatient Infusion Therapy, A Review of the …
Summary
Personalized Decision-Making for Optimal Outcomes
Selecting the appropriate infusion setting is a collaborative process involving:
- Comprehensive Assessments: Evaluating clinical, environmental, and personal factors.
- Patient-Centered Approach: Prioritizing patient preferences and quality of life.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Engaging healthcare teams to ensure cohesive care plans.
Effective infusion management is critical for improving patient outcomes and enhancing satisfaction in care delivery.
Better practices include streamlining workflows, ensuring staff are well-trained in the latest techniques, and leveraging technology like smart pumps to reduce errors.
For example, research shows that using advanced infusion systems can lower medication errors by up to 60%, emphasizing the importance of innovation.
Providers should also focus on tailoring treatments to individual needs, from precise dosing to minimizing patient discomfort during procedures.
Collaboration between physicians, nurses, and management teams is key to maintaining efficiency while prioritizing patient safety.
By adopting these strategies, healthcare teams can navigate the complexities of infusion therapy with confidence, delivering higher-quality care and optimizing results for patients.



