Implementing a home infusion program represents a strategic evolution in patient-centered care—bridging the gap between clinical excellence and the comfort of home.
Driven by the shift to value-based care and patient demand for convenient, safe options, a strong home infusion program offers significant advantages.
Better patient experience, efficient resource use, and improved organizational outcomes are just a few examples of such advantages.
This consolidated guide synthesizes two detailed draft versions into a single, streamlined blueprint.
You’ll find clear, actionable steps, expert insights, and real-world examples—perfect for infusion nurses, physician assistants, clinical leaders, and healthcare executives alike.
Why Home Infusion Matters
Home infusion therapy delivers medications intravenously or subcutaneously in patients’ residences, marrying clinical precision with convenience.
Its value proposition spans multiple dimensions:
Enhanced Patient Care
Effective infusion management begins with prioritizing patient-centered care.
Home infusion therapy has emerged as a best practice, offering convenience while reducing hospital-associated risks.
Patients benefit from avoiding lengthy travel and wait times, while studies reveal that outcomes like adherence and satisfaction often match or surpass those in outpatient settings.
For healthcare teams, leveraging technology such as automated infusion pumps and remote monitoring ensures precision and safety.
Clear communication is key—educating patients on proper techniques and setting realistic expectations can prevent complications.
Collaboration across multidisciplinary teams strengthens care delivery, aligning clinical standards with patient needs.
A notable example: implementing real-time data sharing between physicians and infusion nurses has been shown to improve treatment adjustments, optimizing both care quality and efficiency.
Market Opportunity
The U.S. home infusion sector is evolving rapidly, offering healthcare professionals an opportunity to enhance care delivery while improving patient outcomes.
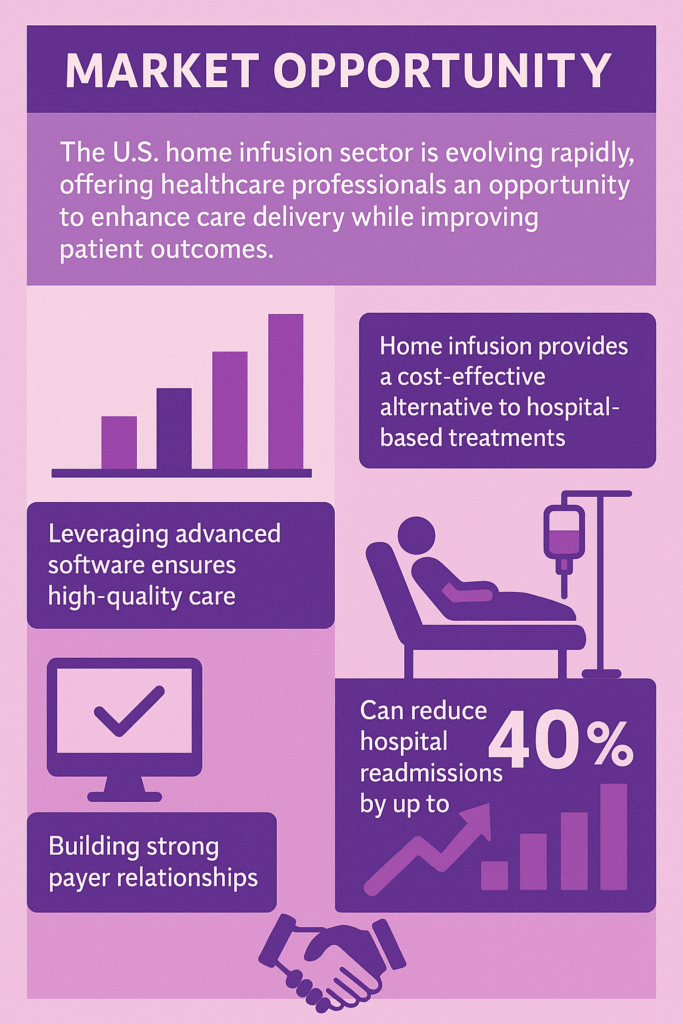
With chronic conditions on the rise and an aging population, home infusion provides a cost-effective alternative to hospital-based treatments.
Best practices include implementing scalable, patient-centered programs that prioritize safety, adherence, and streamlined workflows.
For example, leveraging advanced software to track medication schedules and patient progress ensures consistent, high-quality care.
Effective communication between physicians, infusion nurses, and management teams is vital to prevent errors and improve coordination.
Research suggests home infusion can reduce hospital readmissions by up to 40%, emphasizing its value in chronic care management.
Building strong payer relationships further strengthens long-term program sustainability.
Building the Foundation
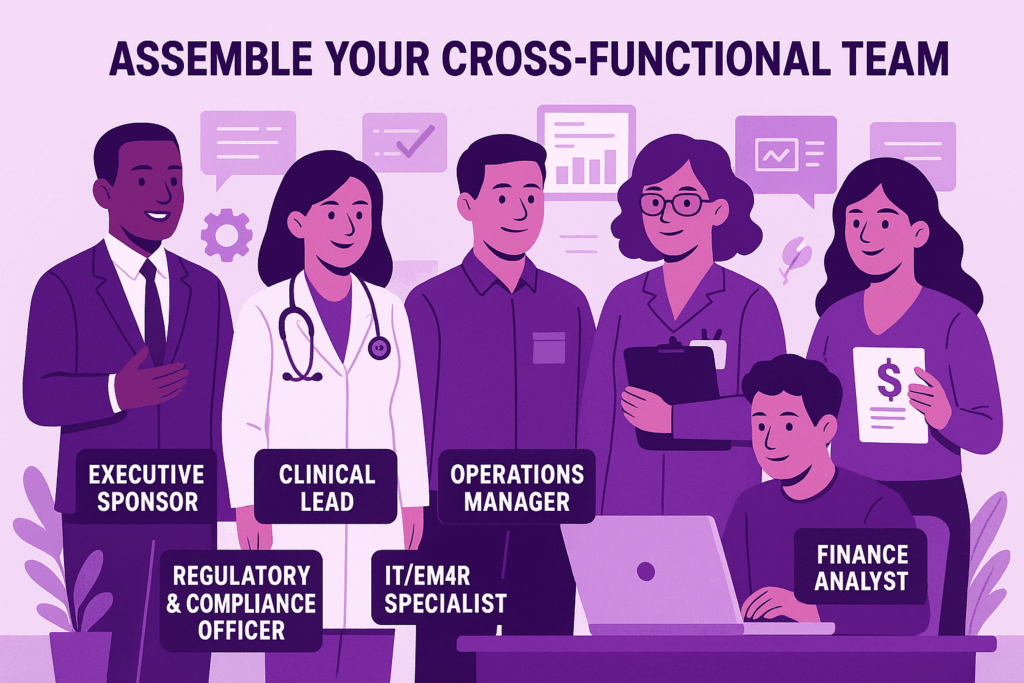
Assemble Your Cross-Functional Team
Success depends on bringing together diverse expertise:
- Executive Sponsor
Champions the program, secures funding, and aligns strategic priorities. - Clinical Lead
Oversees protocol development, safety governance, and clinical training. - Operations Manager
Manages logistics, vendor relationships, and day-to-day workflows. - Regulatory & Compliance Officer
Navigates state pharmacy laws, USP standards (<797>/<800>), and CMS Conditions of Participation. - IT/EMR Specialist
Integrates infusion documentation, telehealth platforms, and analytics dashboards. - Finance Analyst
Constructs cost models, ROI projections, and sensitivity scenarios.
With a skilled team in place, each member contributing their specialized expertise, the foundation for operational excellence and regulatory adherence is firmly established.
This collaborative framework ensures that all aspects of the organization function smoothly, from protocol execution to financial analysis.
Building on this robust structure, the next section will explore the strategies and initiatives driving growth and innovation within the organization.
Conduct Market Analysis
Patient Population Profiling
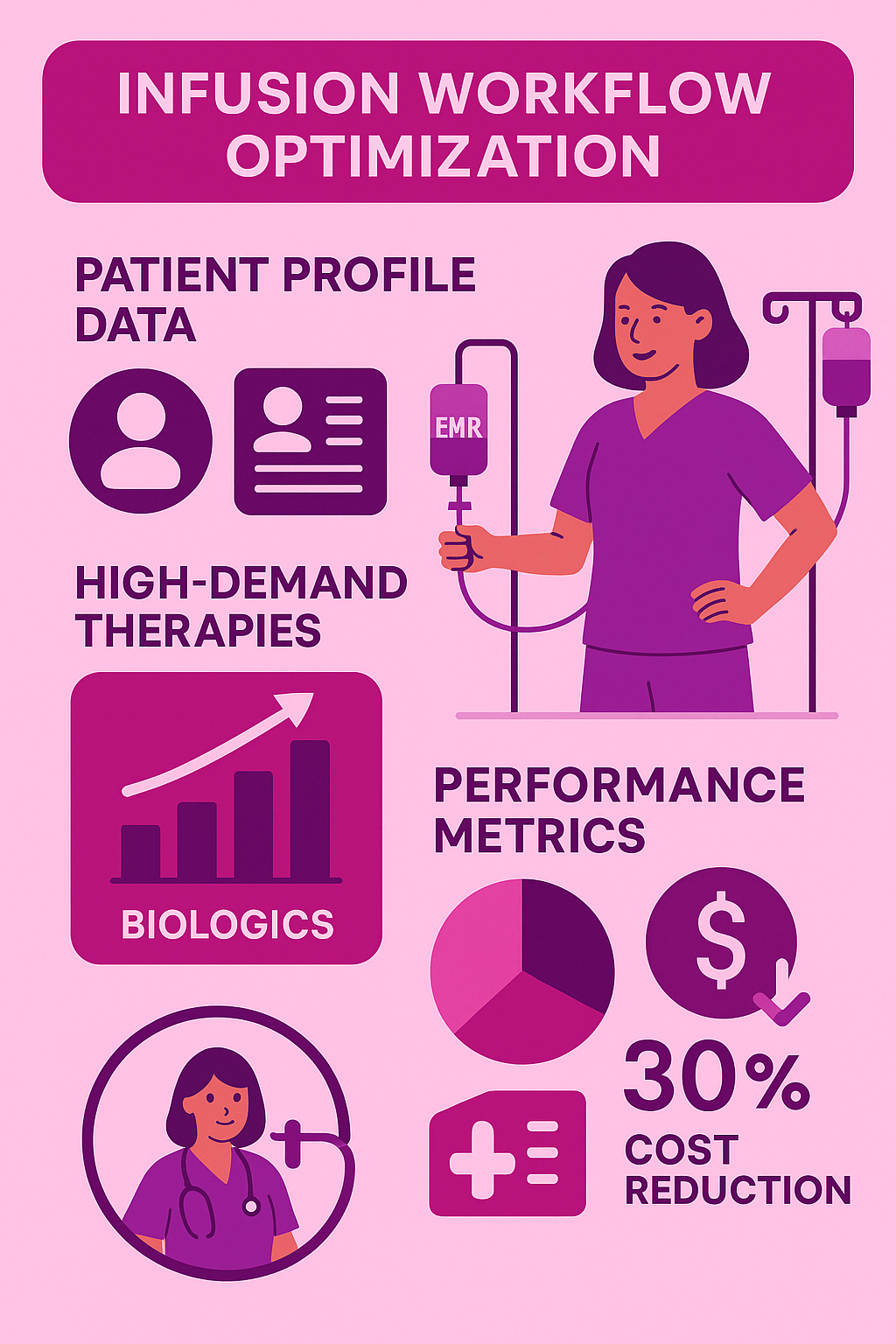
Analyzing historical infusion volumes by therapy category—such as antibiotics, biologics, and nutrition—offers a strategic way to optimize home infusion delivery services.
By identifying high-demand therapies, healthcare teams can prioritize resources where they are most impactful, improving patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
For example, biologics, which are projected to make up 32% of global drug spending by 2027, often require specialized handling and personalized care plans, making them ideal candidates for home infusion when properly managed.
Best practices include leveraging data analytics to track therapy trends and collaborating closely with infusion nurses to ensure safe administration in non-hospital settings.
Tailoring services to high-yield categories not only reduces hospital readmissions but also enhances patient satisfaction by delivering convenience without compromising quality.
Referral Network Engagement

Effective infusion management requires a collaborative approach that prioritizes patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
Engaging a multidisciplinary team, including physicians, infusion nurses, and physician assistants, ensures seamless care delivery while minimizing errors.
One best practice is maintaining clear communication channels between prescribers and infusion centers, reducing delays in treatment initiation.
For example, implementing electronic health records (EHR) systems to track infusion schedules and patient progress can significantly enhance workflow efficiency.
Additionally, regular staff training on the latest infusion protocols and equipment ensures high-quality care and compliance with safety standards.
Studies show that well-coordinated infusion services improve patient satisfaction and reduce hospital readmissions, making proper management a critical factor in achieving better clinical outcomes.
Geographic and Regulatory Mapping
Effective infusion management requires precision, collaboration, and a deep understanding of patient needs.
Mapping patient locations against state licensure boundaries and travel distances is critical to ensuring compliance with regulations and optimizing care delivery.
For instance, adhering to jurisdictional requirements can prevent costly delays and ensure treatments are administered without legal complications.
Best practices include leveraging technology to track patient proximity to infusion centers, streamlining scheduling, and minimizing travel times.
This not only enhances patient satisfaction but also reduces operational inefficiencies.
Did you know that strategic planning in infusion workflows can improve patient adherence rates by up to 30%?
Develop a Compelling Business Case
Cost Comparison
Effective infusion management requires balancing patient outcomes, cost efficiency, and operational workflows.
Facility-based infusions can cost between $600–$1,200 per session, creating financial pressure for both patients and healthcare systems.
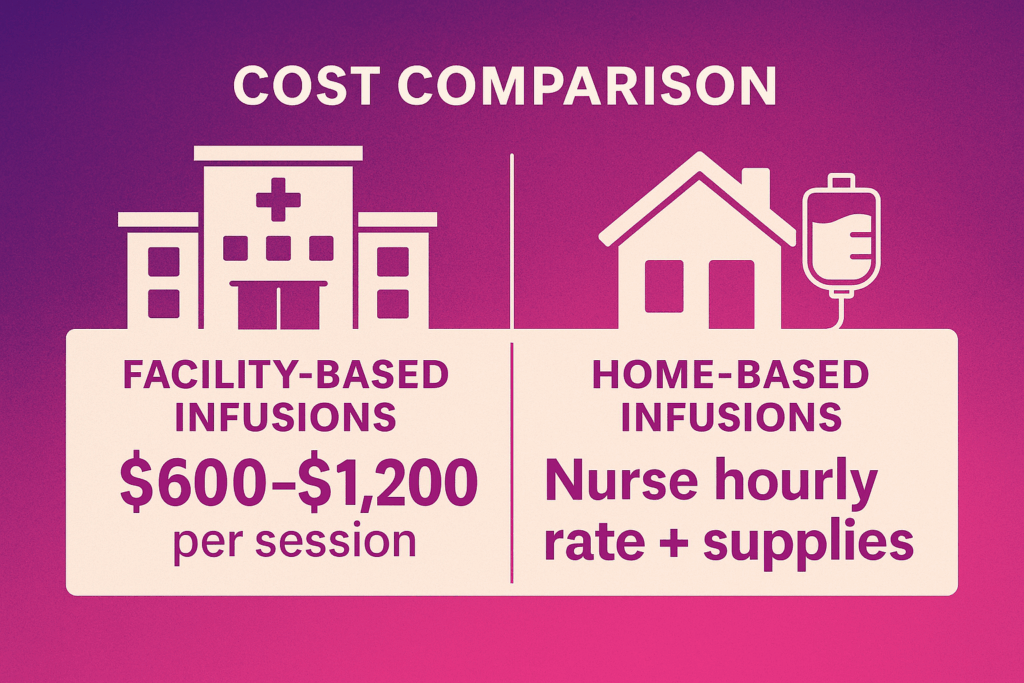
Shifting to home-based infusion models offers a cost-effective alternative, combining nurse hourly rates with minimal supply expenses.
Beyond cost savings, home infusions enhance patient convenience, reduce hospital-acquired infection risks, and improve adherence to treatment plans.
Best practices include thorough patient screening for eligibility, clear communication between care teams, and leveraging technology like remote monitoring to ensure safety and efficacy.
By adopting a hybrid approach—offering facility-based care for complex cases and home infusions for stable patients—healthcare teams can optimize resources while delivering high-quality, patient-centered care.
Revenue Modeling
Effective infusion management is vital for ensuring patient safety, optimizing clinical outcomes, and improving operational efficiency.
Incorporating CPT codes like 96413 and 96365 for infusion services enables accurate billing and reimbursement, streamlining administrative workflows.
Best practices include offering thorough staff training on infusion protocols, maintaining accurate documentation, and leveraging technology for remote monitoring to enhance care coordination.
For instance, integrating telehealth visits can improve patient engagement and identify complications early, reducing hospital readmissions.
According to recent studies, remote monitoring has been shown to improve adherence to treatment plans, especially in chronic disease management.
By fostering a collaborative approach among physicians, infusion nurses, and healthcare teams, you can create a seamless infusion experience that benefits both patients and providers.
ROI

Effective infusion management demands a balance between clinical excellence and operational efficiency.
To achieve success, aim to break even within 12–18 months by optimizing resource utilization and patient flow.
Stress-test your financial model to account for fluctuations in patient volume, payer mix, and reimbursement policies, as these factors can significantly impact profitability.
Implementing standardized protocols and leveraging technology, such as infusion scheduling software, can reduce wait times and improve patient satisfaction.
Additionally, fostering collaboration among physicians, infusion nurses, and administrative teams ensures seamless care delivery.
According to recent studies, clinics that prioritize staff training and data-driven decision-making report a 20% improvement in operational efficiency.
Regulatory Essentials
Certifications

State Pharmacy Permits
Effective infusion management relies on compliance, safety, and streamlined operations.
Securing state pharmacy permits is a critical step for practices delivering sterile compounded medications.
These permits ensure adherence to USP <797> and <800> standards, which govern sterile preparations and hazardous drug handling.
Regular environmental monitoring and media-fill validations are non-negotiable best practices to maintain safety and quality.
For example, conducting monthly environmental checks can significantly reduce contamination risks, protecting both patients and staff.
By prioritizing compliance with state and federal regulations, healthcare teams can focus on delivering high-quality infusion therapy while minimizing legal and operational risks.
Staying proactive in permit management safeguards your practice’s reputation and ensures uninterrupted care for patients.
Home Health Agency Certification
Effective infusion management requires a balance of clinical precision, regulatory compliance, and patient-centered care.

Best practices include developing robust protocols for medication preparation and administration to minimize errors and ensure safety.
Collaboration among physicians, infusion nurses, and physician assistants fosters seamless communication, leading to better patient outcomes.
One key consideration is integrating electronic health records (EHRs) to track infusion schedules and monitor patient responses in real time.
According to recent studies, facilities that adopt standardized infusion workflows see a 25% reduction in adverse events.
Additionally, training staff on the latest infusion techniques and regulatory updates, such as Medicare billing for home health services, ensures compliance and financial sustainability.
Prioritizing these strategies enhances care delivery and operational efficiency.
Accreditation

Effective infusion management requires a balance of clinical excellence, operational efficiency, and patient-centered care.
Best practices include implementing robust protocols to minimize medication errors, leveraging technology such as smart pumps for precise dosing, and conducting regular staff training to stay updated on evidence-based guidelines.
Accreditation from organizations like The Joint Commission or ACHC can significantly enhance quality standards and open doors to payer partnerships, strengthening your reputation and financial sustainability.
For example, facilities with ACHC accreditation often report smoother insurance negotiations and improved patient trust.
Additionally, fostering interdisciplinary collaboration—between physicians, infusion nurses, and PAs—enhances workflow and reduces delays in treatment.
Prioritizing these strategies can optimize outcomes, reduce costs, and elevate the overall infusion experience.
Policy and Procedure Framework
Craft a comprehensive policy suite tailored to home infusion:
| Policy Area | Core Components |
| Sterile Compounding | Cleanroom SOPs, personnel training, environmental monitoring |
| Patient Assessment | Admission criteria, home safety checklists, informed consent |
| Infusion Administration | Order verification, pump programming, aseptic setup |
| Emergency Response | Adverse event algorithms, escalation steps, 24/7 on-call coverage |
| Infection Control | PPE protocols, spill management, sharps disposal |
| Telehealth & Data Security | HIPAA-compliant platforms, session documentation, trigger thresholds |
| Quality Assurance | Incident reporting, chart audits, performance dashboards |
Payer Compliance Workflows

Prior Authorization Automation
Effective infusion management is critical to delivering safe and efficient patient care while optimizing operational workflows.
Best practices include streamlined scheduling, robust patient screening, and adherence to evidence-based protocols.
For example, ensuring pre-infusion allergy assessments can significantly reduce adverse reactions, which occur in approximately 10-20% of infusion therapy cases.
Collaborative communication between providers, infusion nurses, and administrators ensures treatment plans are aligned with clinical goals and patient needs.
Leveraging advanced infusion pumps and automated software enables precise dosing and reduces human error, enhancing patient safety.
It’s also essential to maintain rigorous infection control practices, from proper catheter care to environmental sanitation, to minimize complications such as sepsis.
By fostering a culture of continuous improvement and data-driven decision-making, healthcare teams can elevate patient outcomes while bolstering team efficiency.
Medical Necessity Documentation
Effective infusion management requires a strategic approach to streamline workflows, reduce errors, and ensure optimal patient care.
One best practice is utilizing templated letters aligned with payer guidelines to minimize denials, which can save significant time and resources.
For instance, clear documentation and adherence to coverage criteria can improve approval rates by up to 30%, according to recent industry data.
Additionally, fostering strong communication among physicians, infusion nurses, and healthcare teams is crucial for seamless coordination.
Regular staff training on protocols and insurance updates helps maintain compliance and efficiency. By prioritizing these steps, teams can enhance patient outcomes, reduce administrative burdens, and focus on delivering high-quality care—a cornerstone of successful infusion management.
Claims Tracking
Effective infusion management requires clear visibility into key metrics like submission status, denial reasons, and appeal outcomes.
Building a centralized dashboard can streamline these processes, enhancing decision-making and patient care.
For example, tracking denial reasons in real time allows teams to identify patterns, address common issues, and reduce delays in treatment.
An intuitive dashboard can also improve collaboration among physicians, infusion nurses, and administrative staff by centralizing data access.
According to recent insights, nearly 30% of claim denials are preventable with better documentation and monitoring tools.
By implementing a robust dashboard solution, healthcare teams can minimize administrative burdens, improve reimbursement rates, and focus more on delivering high-quality care. Integration with existing workflows is key to maximizing efficiency and outcomes.
Clinical Safety

Therapy-Specific Order Sets
Develop standardized order templates for each therapy line:
Antibiotics
Effective infusion management hinges on understanding dosing frequencies, stability parameters, and lab monitoring requirements.
Tailoring dosing schedules to a patient’s specific needs ensures therapeutic efficacy while minimizing adverse effects.
Stability parameters—such as storage conditions and preparation timelines—are equally vital to maintain medication potency, particularly for biologics or temperature-sensitive infusions.
Regular lab monitoring allows clinicians to track patient progress and detect potential complications early, enhancing safety and outcomes.
For example, timely lab reviews can identify shifts in renal or hepatic function, guiding necessary adjustments to dosing.
Adopting these best practices not only optimizes patient care but also improves workflow efficiency for infusion teams.
Integrating data-driven tools or AI software can further streamline the process, ensuring seamless management.
Biologics
Effective infusion management requires precision and clarity, particularly when comparing RN-administered and patient self-administration pathways for reconstitution.
For RN-administered infusions, ensuring proper training on guidelines and aseptic techniques is critical to minimize errors and maximize patient safety.
This pathway often allows for more consistent monitoring, reducing complications such as improper mixing or dosing.
On the other hand, patient self-administration can empower individuals and improve compliance, especially for chronic conditions, but it demands robust education and clear instructions.
A study from The Journal of Infusion Nursing highlights that personalized training can improve patient adherence by up to 40%.
Balancing these pathways requires evaluating patient capability, resource availability, and clinical oversight to optimize outcomes while maintaining safety and efficacy.
Parenteral Nutrition
Effective infusion management requires careful attention to macronutrient calculations, weight-based adjustments, and pump settings to ensure optimal patient outcomes. Tailoring infusion therapy to individual needs starts with precise macronutrient assessment, balancing energy requirements with clinical goals.
Weight-based adjustments, particularly for pediatric or critically ill patients, are crucial to avoid under- or over-infusion, which can lead to complications like refeeding syndrome or fluid overload.
Proper pump settings enhance accuracy, minimize errors, and support consistent delivery, particularly in high-risk scenarios such as TPN administration.
Research shows that advanced infusion pumps with customizable alerts reduce medication errors by up to 60%.
By integrating these best practices, healthcare teams can deliver safer, more effective care.
Pain Management
Effective infusion management requires a multifaceted approach to ensure patient safety and treatment success.
Implementing controlled-substance regulations helps prevent misuse and ensures compliance with legal standards, protecting both patients and healthcare providers.
Incorporating pump lockout features into infusion devices minimizes the risk of medication errors by preventing unauthorized dosage changes, a critical safeguard in high-risk environments.
Equally important is providing overdose education to clinical teams, empowering them to recognize early warning signs and respond swiftly during emergencies.
For example, studies show that well-trained staff can reduce adverse drug events by up to 30%.
By combining these best practices, healthcare teams can optimize patient care while maintaining safety, compliance, and efficiency in infusion therapy.
Patient Selection and Education
Patient selection and education are pivotal in ensuring the success and safety of infusion therapy.
Properly identifying candidates for treatment involves a thorough assessment of their medical history, current health status, and potential risk factors.
Equally important is equipping patients with the knowledge and tools they need to actively participate in their care.
Empowering patients through education not only enhances compliance but also fosters a sense of confidence and collaboration between patients and healthcare providers, ultimately leading to improved outcomes and a higher standard of care.
- Inclusion Criteria
- Stable vital signs, low reaction risk, reliable home support.
- Exclusion Criteria
- Uncontrolled comorbidities, unsafe living conditions, lack of caregiver assistance.
- Onboarding Workflow
- Conduct teach-back sessions covering pump operation, IV site care, and emergency protocols. Provide a welcome packet with infusion schedules, contact cards, and patient handbooks.
Emergency Response
Effective monitoring and a well-structured emergency response plan are critical components of ensuring patient safety and successful outcomes.
This section outlines the procedures for regularly assessing patient progress, recognizing potential complications, and responding swiftly to any emergencies that may arise during the treatment process.
By implementing these protocols, care teams can mitigate risks and provide timely interventions, fostering greater confidence for both patients and caregivers.
- Initial Visit
- Perform baseline vitals, inspect IV access, confirm supply delivery, and reinforce patient education.
- Ongoing Monitoring
- Schedule RN or LPN visits (daily to weekly based on therapy), supplemented with telephonic or telehealth check-ins.
- Emergency Protocols
- Maintain a 24/7 on-call RN line. Establish clear escalation pathways to ED, primary care, or clinical leads.
Operational Logistics
Supply Chain
Effective infusion management requires a strategic approach to ensure patient safety, streamline workflows, and reduce waste.
Partnering with licensed distributors is essential for reliable batch shipments and emergency overnight delivery, minimizing disruptions to patient care.
Implementing robust inventory controls, such as barcoding and EMR integration, provides real-time stock visibility while tracking expirations, helping to prevent costly errors and ensure compliance.
For biologics and nutrition solutions, cold chain management is critical.
Using validated insulated packaging and temperature monitoring safeguards sensitive products during transit, preserving efficacy.
According to industry reports, improper cold storage contributes to 20% of medication spoilage globally, underscoring the importance of meticulous handling.
By adopting these best practices, healthcare teams can enhance efficiency and deliver optimal care.
Communication
Effective infusion management hinges on streamlining operations to optimize care delivery and improve patient outcomes.
Centralized scheduling is a cornerstone of efficiency, enabling healthcare teams to cluster visits geographically.
By reducing nurse travel time, organizations save valuable hours and improve care access.
Pair this strategy with automated reminders—sending SMS or voice notifications 24–48 hours before appointments.
This simple step can significantly cut no-show rates, ensuring patients stay on track with treatment plans.
Additionally, leveraging real-time updates enhances patient satisfaction and operational transparency.
Providing live ETA tracking through mobile apps or web portals keeps patients informed and reduces uncertainty.
A well-integrated approach like this not only boosts efficiency but fosters trust between patients and providers, creating a smoother, more reliable infusion experience.
EMR Analytics

Documentation Templates
Integrating home infusion assessments, logs, and visit notes directly into the EMR streamlines workflows and enhances care coordination.
For infusion nurses and healthcare teams, this approach ensures real-time access to critical patient data, reducing errors and improving decision-making.
A best practice is to use EMR systems designed to support seamless documentation, enabling clinicians to track infusion outcomes and medication adherence efficiently.
Studies show that EMR integration can cut documentation time by up to 30%, freeing providers to focus more on patient care.
Additionally, embedding infusion data supports compliance with regulatory standards while improving communication across multidisciplinary teams.
Ultimately, this strategy not only optimizes operational efficiency but also reinforces patient-centric care in infusion management.
Interoperability
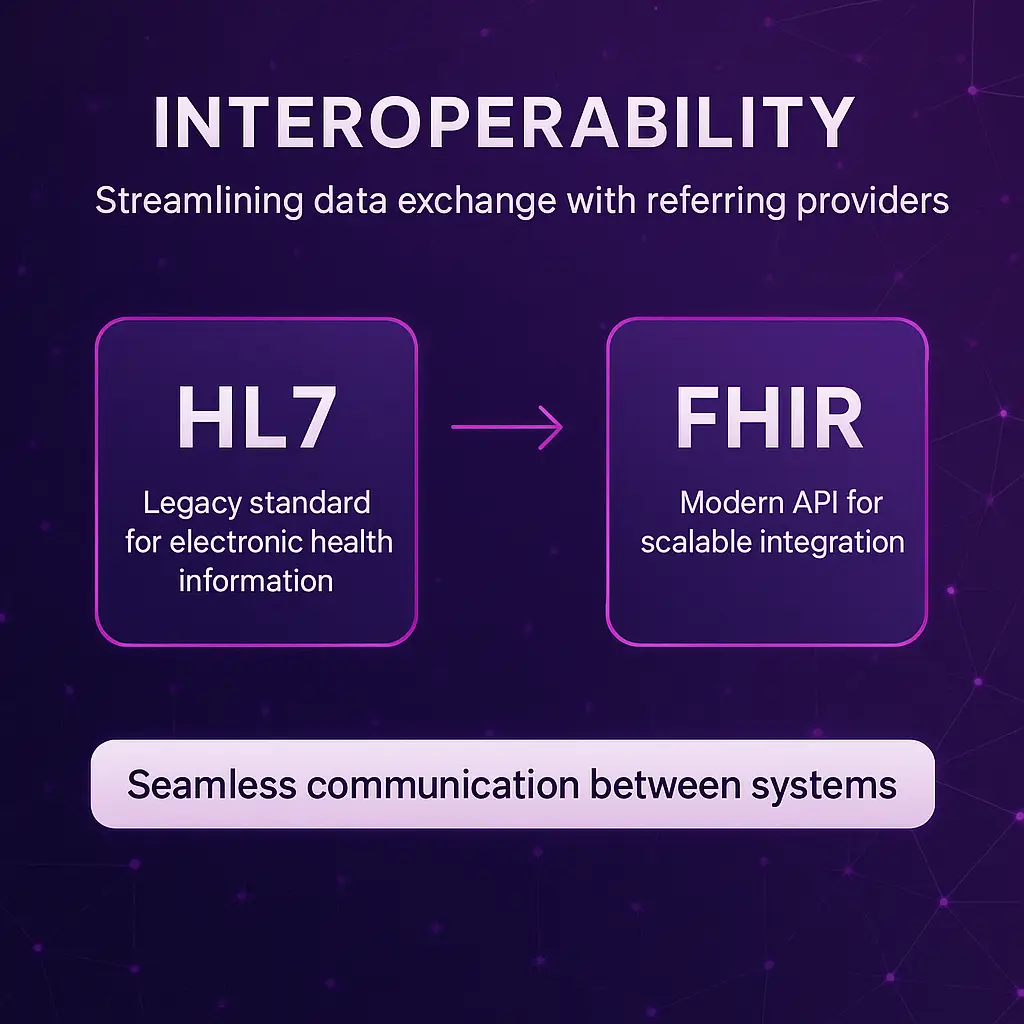
Streamlining data exchange with referring providers through HL7 or FHIR interfaces is a game-changer for infusion management.
These standards enable seamless communication between systems, ensuring accurate, real-time information sharing—critical for improving patient outcomes.
For example, when managing infusion therapies for complex cases, having immediate access to patient histories, lab results, or prior treatment notes reduces errors and delays.
HL7 interfaces can automate key workflows, while FHIR’s modern API approach supports scalability and integration across diverse EHR systems.
Best practices include ensuring data privacy compliance, implementing regular interface testing, and collaborating with IT teams for smooth transitions.
By embracing these tools, healthcare teams can focus more on delivering safe, efficient, and personalized care.
Performance Dashboards
Effective infusion management relies on tracking key performance metrics like on-time start rates, reaction incidents, readmissions, and patient feedback.
By closely monitoring these data points, healthcare teams can identify patterns, address inefficiencies, and enhance patient outcomes.
For example, improving on-time start rates not only boosts patient satisfaction but also streamlines resource utilization.
Reviewing reaction incidents helps refine protocols to reduce adverse events, fostering a safer clinical environment.
Patient feedback is equally critical—it provides actionable insights to tailor care practices.
Regular analysis of these metrics ensures continuous improvement and empowers teams to deliver high-quality, patient-centered infusion therapy.
Staffing, Training and Culture
- Staffing Model
- Hire RNs, LPNs, and pharmacists experienced in home infusion, plus support roles in scheduling, logistics, and billing.
- Competency Framework
- Implement role-specific training modules on aseptic technique, pump programming, emergency response, and patient education.
- Ongoing Education
- Conduct quarterly in-services, annual competency assessments, and root-cause analyses for incidents and near-misses.
- Safety Culture
- Promote anonymous error reporting, regular team huddles, and PDSA (Plan–Do–Study–Act) cycles to foster transparency and innovation.
Building a robust home infusion program requires a strategic approach to staffing, training, and safety.
Start with a comprehensive staffing model by hiring experienced RNs, LPNs, and pharmacists, as well as support staff for scheduling, logistics, and billing, ensuring seamless operations and patient care.
Develop a competency framework to provide role-specific training on critical skills like aseptic technique, pump programming, emergency response, and patient education, equipping staff to handle complex scenarios confidently.
Prioritize ongoing education with quarterly in-services, annual competency assessments, and root-cause analyses to address incidents, fostering continuous improvement.
Lastly, establish a strong safety culture by encouraging anonymous error reporting, regular team huddles, and using PDSA cycles to promote transparency, innovation, and accountability across the team.
Patient Engagement
- Personalized Education
- Provide multimedia resources—instructional videos, mobile tutorials, and illustrated guides—to reinforce teach-back learning.
- Language & Accessibility
- Offer interpreter services, translated materials, and adaptive pump devices for patients with mobility or dexterity challenges.
- Continuous Support
- Schedule telehealth check-ins for complex therapies; maintain a 24/7 infusion RN hotline; deploy post-therapy satisfaction surveys to capture feedback and drive improvements.
- Transportation Assistance
- Partner with ride-share or community services to facilitate supply pickups and clinic-based tasks when needed.

Empowering patients through personalized, accessible, and continuous support is critical in modern healthcare.
Start by offering tailored education: multimedia tools like videos, illustrated guides, and mobile tutorials can boost understanding and retention, especially when paired with teach-back methods.
For diverse patient populations, language and accessibility solutions—such as interpreter services, translated materials, and adaptive devices for mobility challenges—ensure equitable care.
Continuous support matters, too.
Telehealth check-ins for complex therapies and a 24/7 infusion nurse hotline provide peace of mind while post-therapy satisfaction surveys offer actionable insights for improvement.
Finally, addressing logistical obstacles like transportation is key.
Collaborate with ride-share programs or community services to simplify clinic visits and supply pickups.
By integrating these strategies, healthcare teams can deliver care that truly meets patients where they are.
Quality Assurance
| Metric Category | Key Performance Indicator |
| Clinical | Infusion reaction rate; readmission rate; infection rate |
| Operational | On-time start percentage; average visit time; supply waste |
| Financial | Cost per infusion; days to reimbursement; denial ratio |
Scaling
Geographic Growth
Expanding into new geographic regions presents an exciting opportunity for growth and innovation, enabling organizations to serve a broader patient population while increasing operational impact.
Successful geographic expansion requires thoughtful, data-driven decision-making and a strategic approach to resource allocation, market analysis, and partnerships.
By leveraging insights from performance metrics, benchmarking standards, and proven improvement cycles, organizations can ensure scalability without compromising service quality.
A well-executed growth strategy not only fosters wider patient access to essential home infusion services but also enhances organizational resilience and adaptability in a competitive market.
The following strategies outline key considerations to guide geographic growth, ensuring seamless implementation and sustainable success in new territories.
Service Line Diversification
Advancements in treatment and monitoring technologies are transforming patient care.
Emerging therapies, such as subcutaneous immunoglobulin, enzyme replacement treatments, and anti-TNF biologics, are expanding clinical pipelines, offering more personalized and effective options for managing complex conditions like autoimmune disorders and rare diseases.
Meanwhile, remote monitoring technologies are redefining how care is delivered.
Wearable sensors and infusion pump telematics allow healthcare teams to detect complications early, reducing the need for frequent in-person visits and improving patient outcomes.
For example, telematics-enabled devices can alert clinicians to potential infusion irregularities, ensuring timely interventions.
Together, these innovations empower providers to deliver proactive, patient-centered care with greater precision and efficiency.
Strategic Partnerships
Strategic partnerships play a pivotal role in driving innovation and enhancing care delivery in modern healthcare.
By fostering collaborations between medical device manufacturers, technology firms, and healthcare providers, these alliances accelerate the development of advanced solutions tailored to patient needs.
For instance, partnerships between wearable technology companies and hospital systems enable seamless data integration, creating a more comprehensive picture of patient health.
Such collaboration ensures that clinicians can make timely, data-driven decisions, improving outcomes and reducing complications.
Additionally, partnerships with artificial intelligence developers open new avenues for predictive analytics, allowing healthcare teams to anticipate trends and intervene early.
These synergistic relationships not only improve operational efficiency but also enable a unified focus on providing personalized, high-quality care, underscoring the importance of collective innovation in transforming the healthcare landscape.
Case Studies

Examining real-world applications provides invaluable insights into the strategies and solutions shaping the future of healthcare.
The following case studies highlight key collaborations and innovations that have successfully addressed complex challenges in the industry.
First, a partnership with a regional health system showcases the development of streamlined referral pathways, resulting in improved patient access and a substantial increase in care coordination.
Next, a value-based agreement with a leading payer demonstrates how data-driven approaches reduced overall healthcare costs while maintaining high-quality outcomes.
Lastly, a collaboration with a telehealth provider and analytics firm reveals the role of advanced technology in boosting patient engagement and operational efficiency.
Each case exemplifies the power of targeted solutions in achieving measurable, impactful results across healthcare ecosystems.
Midwest Regional Health System
- Challenge: Elevated 30-day readmission rates for IV antibiotics.
- Solution: Launched a centralized pharmacy hub, standardized care protocols, and driver-managed supply drops.
- Outcome: 35% reduction in readmissions; 92% patient satisfaction.
Rural Health Collaborative
- Challenge: Transportation barriers impeded access for remote populations.
- Solution: Deployed mobile infusion vans and tele-nursing for virtual assessments.
- Outcome: 48% increase in patient volume within six months; expanded service hours including evenings and weekends.
Implementation Checklists
Pre-Launch
- Secure executive sponsorship
- Finalize state licensure and accreditation
- Complete policy and protocol approvals
- Build EMR workflows and scheduling systems
- Recruit and train initial staffing cohort
First 90 Days
- Launch pilot with 10–20 patients
- Monitor KPIs weekly; refine processes
- Hold interdisciplinary debrief meetings
- Scale patient education and engagement tools
Summary

This guide serves as a comprehensive framework for successfully launching and scaling a new healthcare initiative.
By securing the necessary approvals, building robust systems, and investing in staff training during the pre-launch phase, organizations can establish a strong foundation.
The first 90 days focus on piloting services, monitoring performance, and refining processes to ensure sustainability and patient satisfaction.
Following this structured approach will help drive impactful outcomes while maintaining operational excellence.



